Author: Sam Kuhn and Ada Acker
Economy-wide breakdown:
- The U.S. labor market has shrugged off the worst predictions of the immediate tariff impacts as employment growth averaged 150,000 per month over a three-month average. Yet, when you look under the hood, warning signs emerge: healthcare and leisure & hospitality own the bulk of job growth while all other major sectors are either flat or have contracted.
- The unemployment rate fell slightly to 4.1% in June, but due to an unfavorable reason: the labor force has begun to contract. In May, 625,000 workers left the labor force. Then the labor force contracted again by 130,000 in June. The shift in U.S. immigration policy has started to materialize throughout the job market, potentially signaling renewed labor shortages.
- On the trade front, a new major trade deadline has been announced: come August 1st, a new set of reciprocal tariffs will be enforced unless a deal with that country has been struck. Policy uncertainty remains elevated, which is souring the mood of consumers and businesses. Until clarity is given on the final path of trade, it is likely that volatility will persist in financial markets, risking bleeding into the broader economy.
- On July 4th, the One Big Beautiful Bill Act (OBBBA) was signed into law marking a significant change in fiscal policy: tax cuts for both businesses and households, boosted funding for immigration enforcement, and reductions in spending for Medicaid and SNAP. Each one of these provisions can alter the difficulty of recruiting by industry, depending on the type of workforce. TK: Read more from our Chief Economist Andrew Flowers to learn more.
Read our economy-wide breakdown of the latest numbers.
Employment Trends
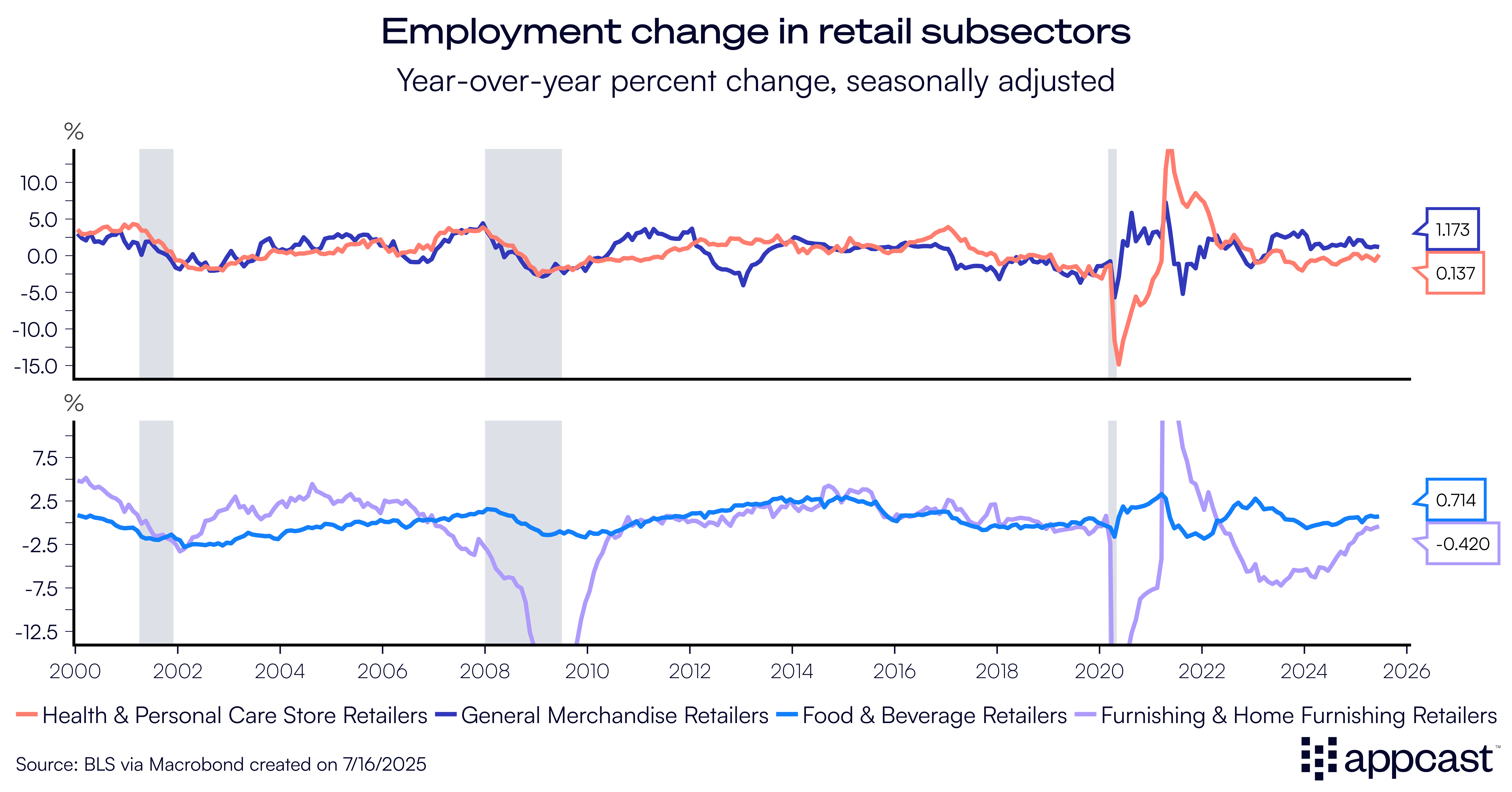
Policy changes in the U.S. have affected inflation and increased consumer pessimism, and the retail sector is on the front lines. However, the sector remains relatively steady, even as consumer spending begins to slow after the bump in the first quarter.
Health & personal care retailers as well as general merchandise retailers have maintained moderately constant employment change over the quarter. The latest data shows a slight increase to 0.1% in employment for health & personal care and a decrease in general merchandise to 1.1%.
Food and beverage retailers also remain rather steady, as employment change maintains a 0.7% increase in employment.
Historically, furnishing & home furnishing have been more sensitive to economic change. The latest data indicates a -0.4% decrease in employment. However, employment change has been on the rise in the subsector, rising from -0.8% year-over-year growth at the end of the first quarter.
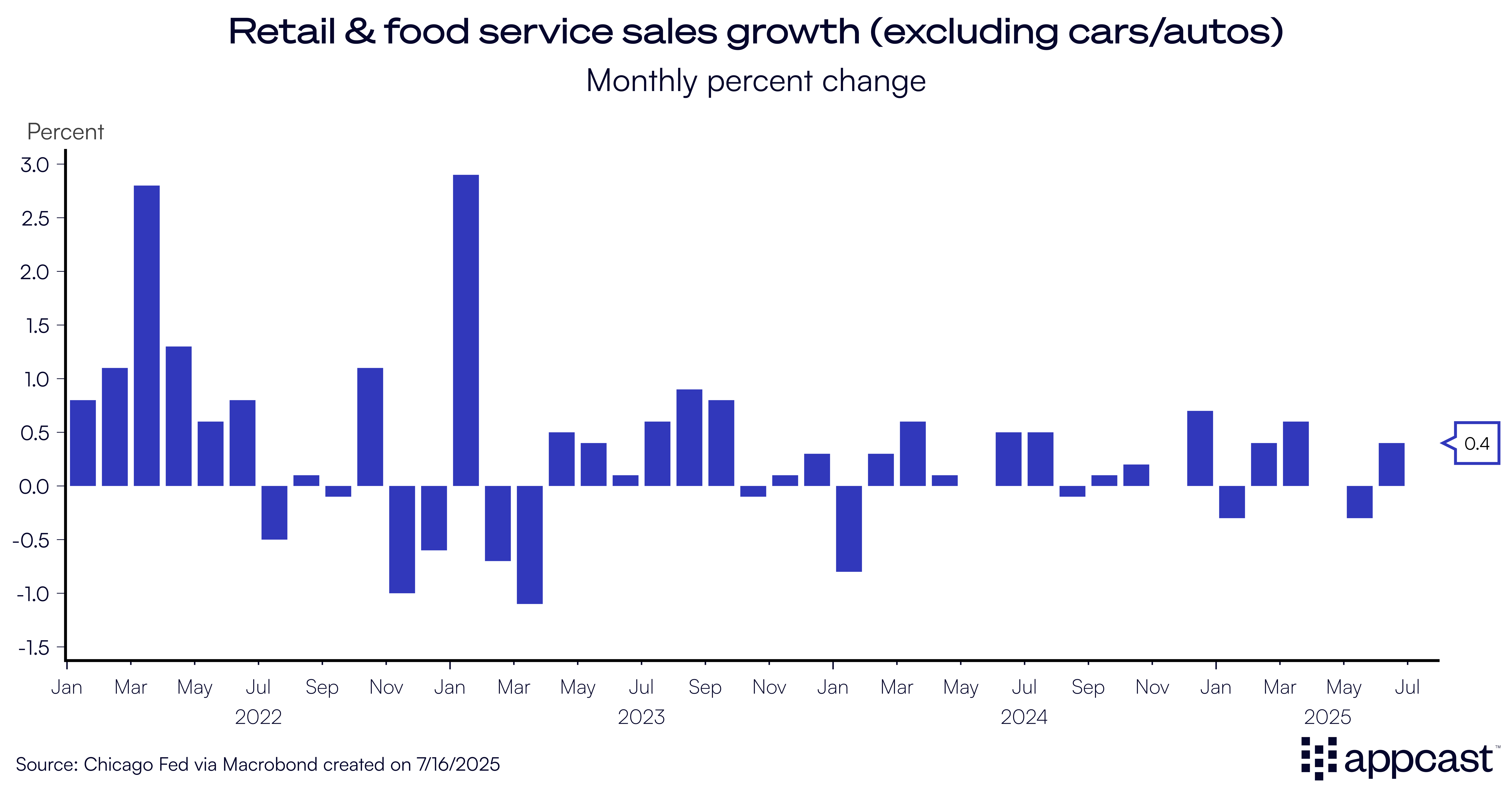
Sales growth within the sector has been rather volatile in the past three years, following a declining trend. 2025 started off with a small spike in sales growth after tariffs were promised and there was an increase in consumer spending, however that trend seems to have died down, with recent growth landing at 0.4%. With more tariffs on the horizon, a further decline in sales growth may be observed; however, growth is likely to remain slightly positive overall.
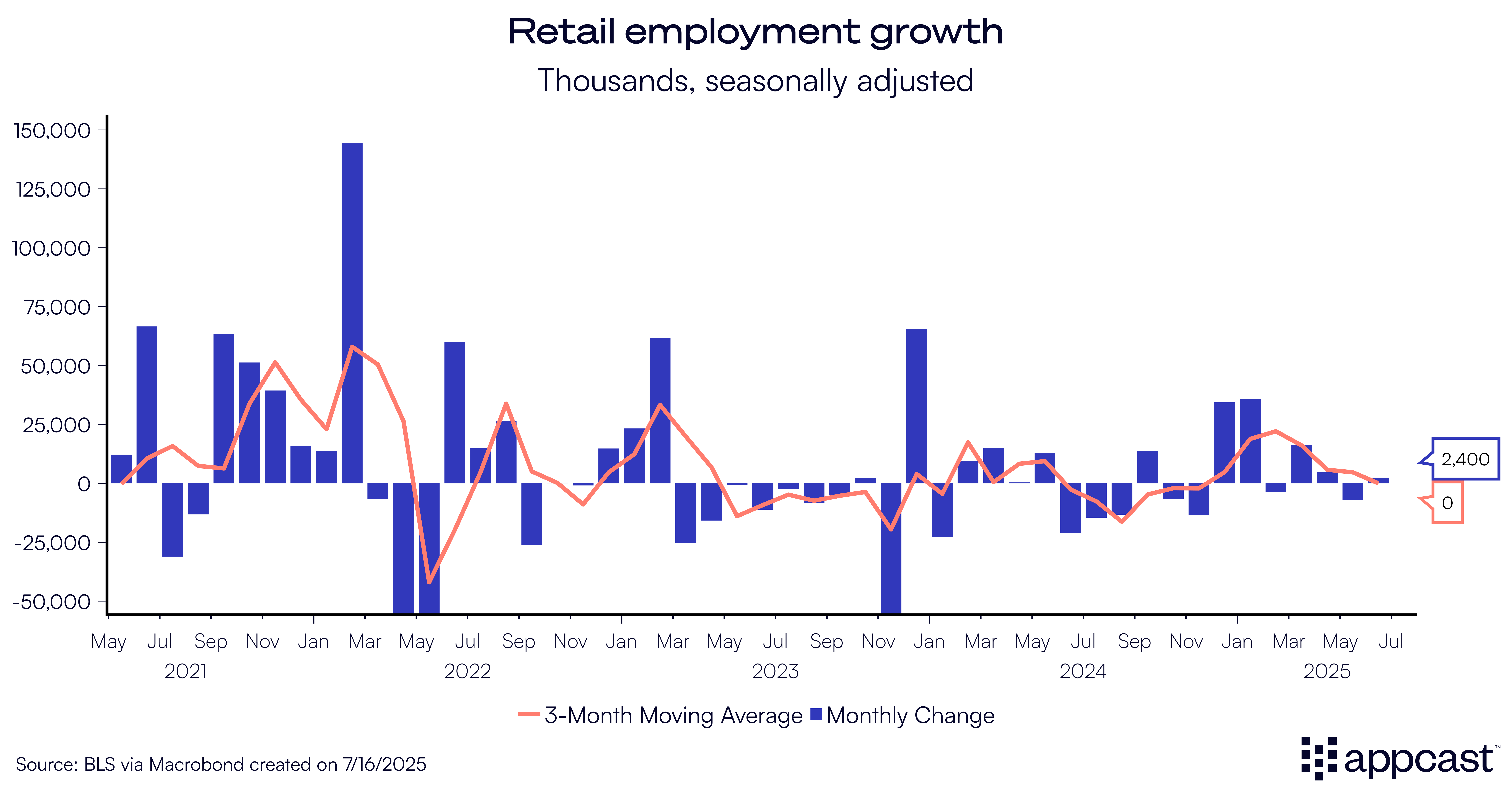
Employment growth took a dip in the second quarter. After positive gains earlier in the year, there was a downward trend leveling out to a 3-month moving average of 0 at the end of the quarter. Growth will likely remain low as the tariffs and consumers’ response settle and finalize.
Wage Trends
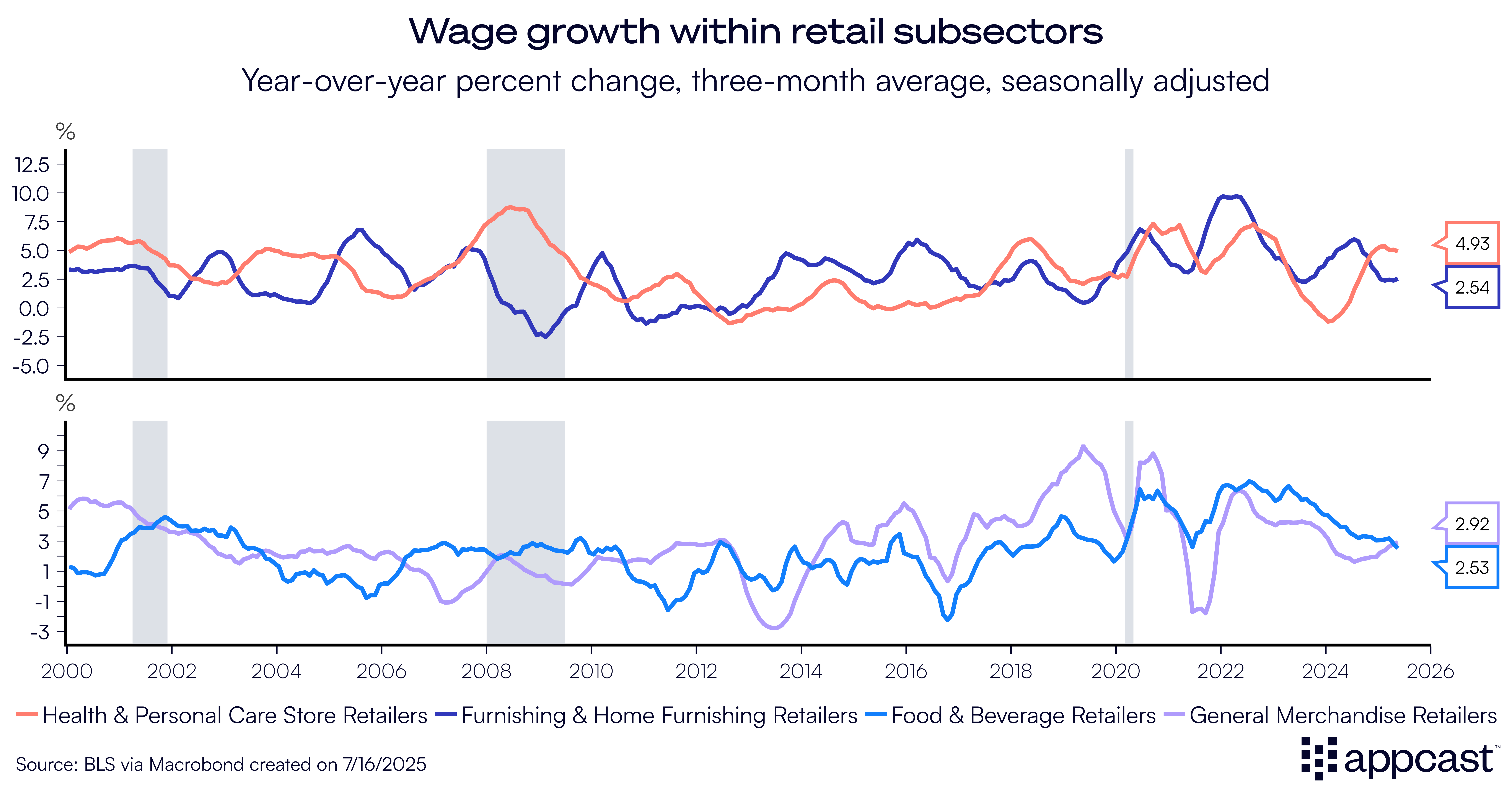
Furnishing & home furnishing workers saw a slight increase and steadying out of wage growth at 2.5% and health & personal care wage growth decreased marginally to 4.9%. The high wage growth indicates continued demand for health and furnishing-related products amongst consumers.
Food & beverage wage growth dropped to 2.5% annual growth while general merchandise remained on the rise, climbing up to 2.9%, showing that consumer demand remains stable.
Overall, wage growth remains relatively stable across all major sectors, indicating that even in recent economic uncertainty and inflation, consumer spending remains steady, if a bit slow.
Openings and Turnover Trends
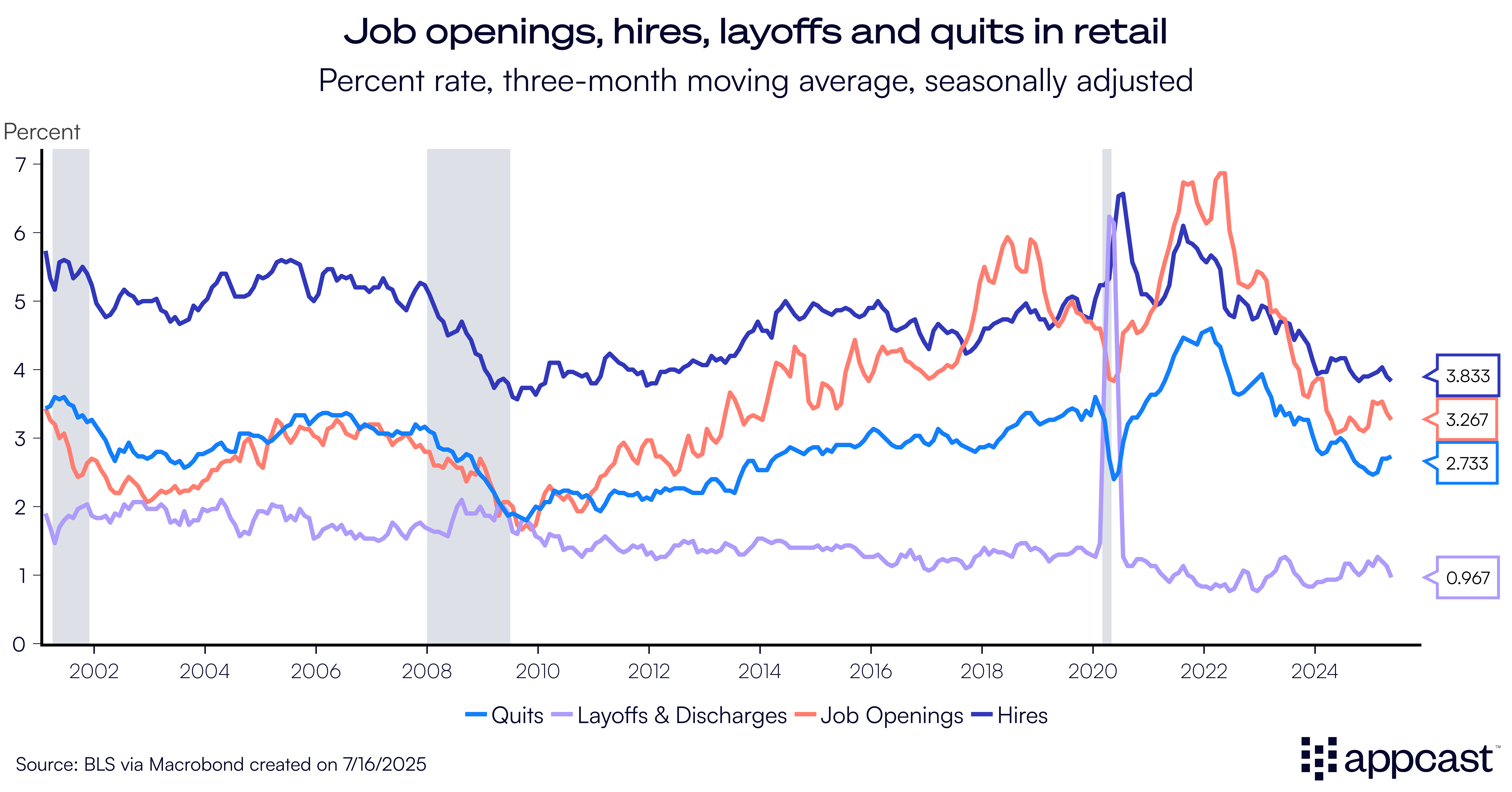
After nearly a year-long downward trend in quitting, this past quarter saw an increase to 2.7%. Job openings and hires have decreased to 3.8% and 3.2%, respectively, after the jump in consumer spending in the last quarter has cooled off. Layoffs remain low and continue to drop, settling at just below 1%, suggesting that employers remain cautious.
For the past year there has been a downward trend in job openings and hires due to the low quit rates. However, quit rates increased marginally over the last quarter while hires and job openings declined. The outlook for the rest of the year is therefore mixed. Normally, an increased quit rate suggests potential for an increase in job openings, but we have not seen if that increase will take effect just yet.
Recruitment Marketing Trends
The term “long” or “ATS apply” refers to the conventional application process, requiring applicants to manually submit their tailored application documents and personal details through the company’s website or an applicant tracking system (ATS). In many cases, applicants are required to create a company-specific account.
On the other hand, “easy apply” refers to a swift application process on a job board, often conducted through a smartphone. With a single click, essential information like the resume is transmitted directly to the company. Due to the simplicity of this application method, easy-apply metrics are not directly comparable to those of the “long” or ATS apply. The metrics are therefore presented separately.
Long Apply
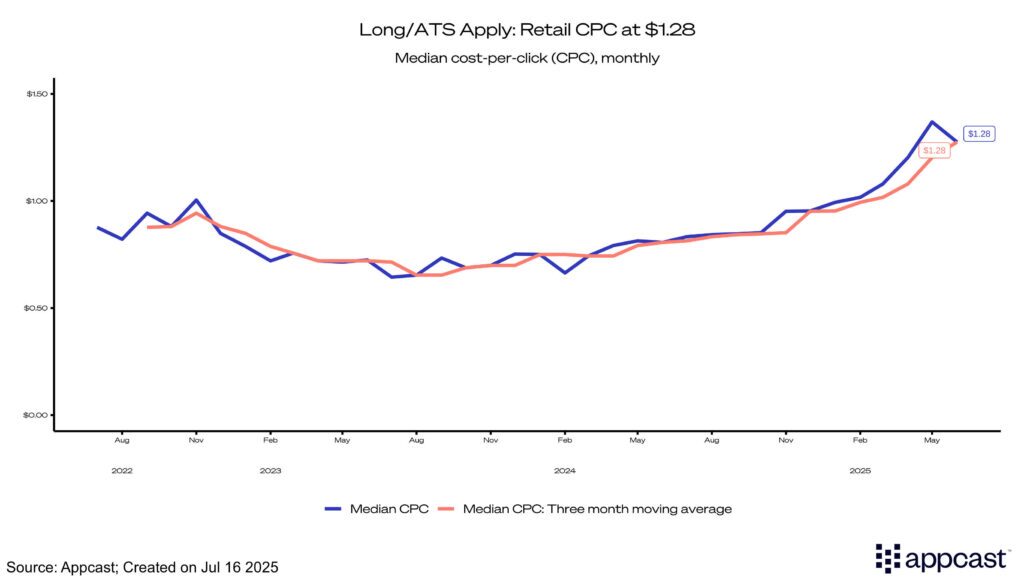
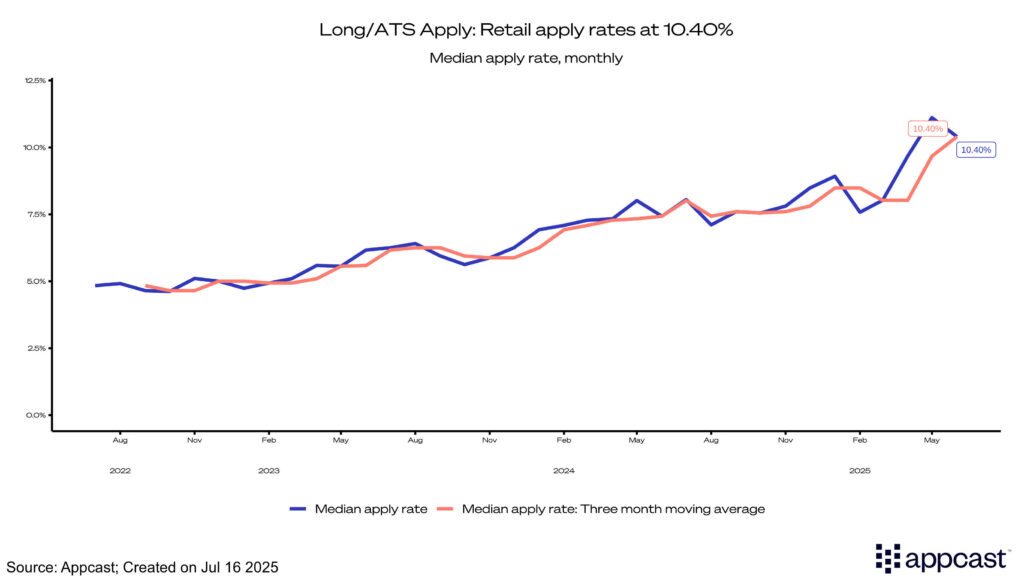
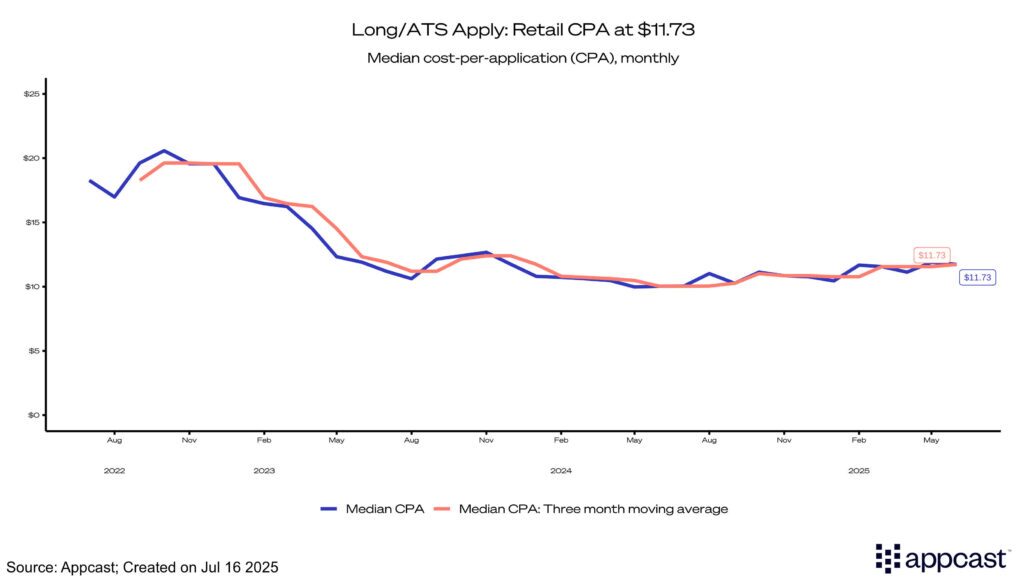
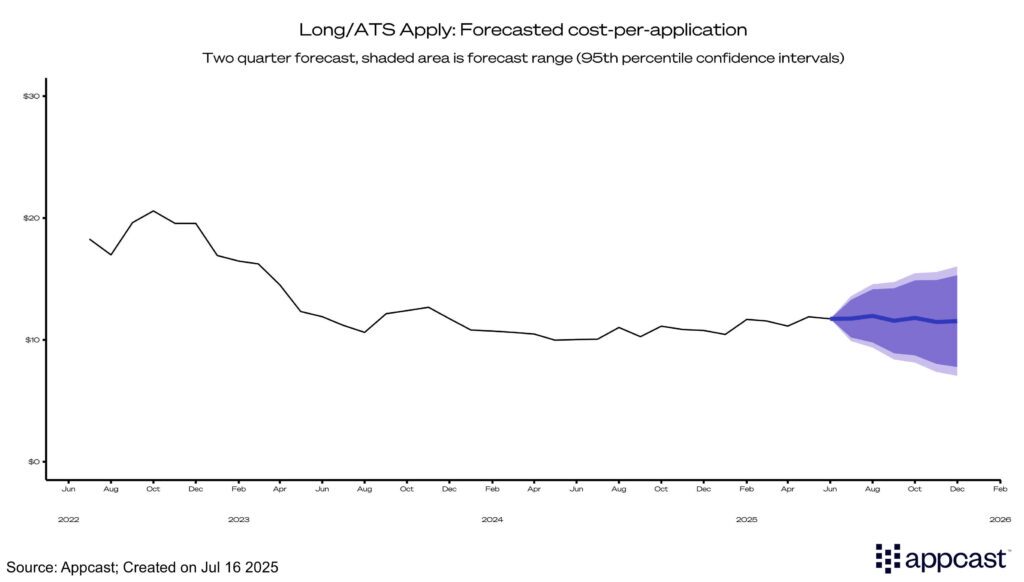
Recruiting costs remain low in the retail industry due to the decrease in job postings as well as an increasing interest from job seekers over the past year. The median cost-per-click (CPC) rose slightly to $1.28, while the median cost-per-application (CPA) held steady at just below $12. Apply rates continued to rise over the second quarter, settling at just over 10%.
Easy Apply
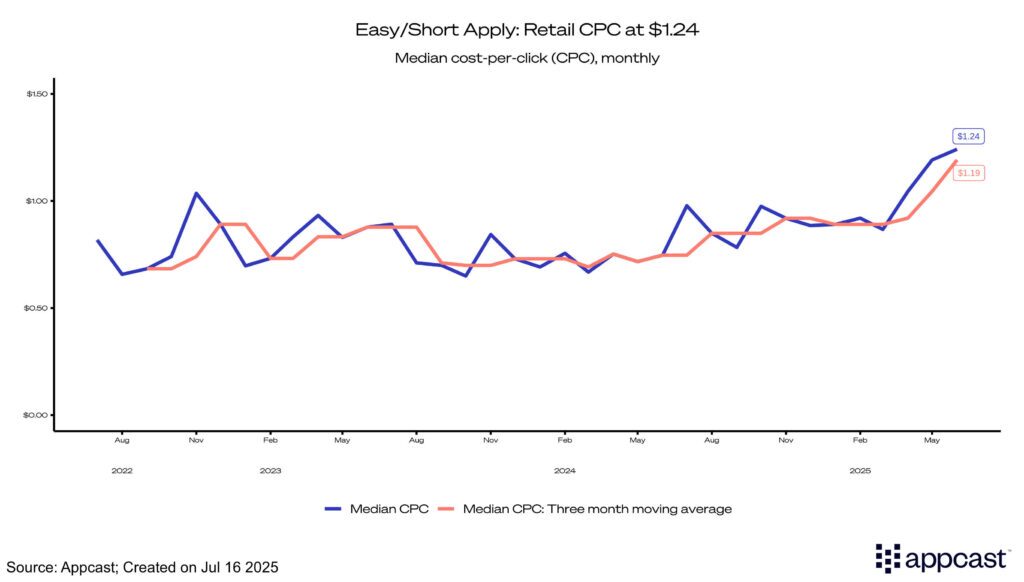
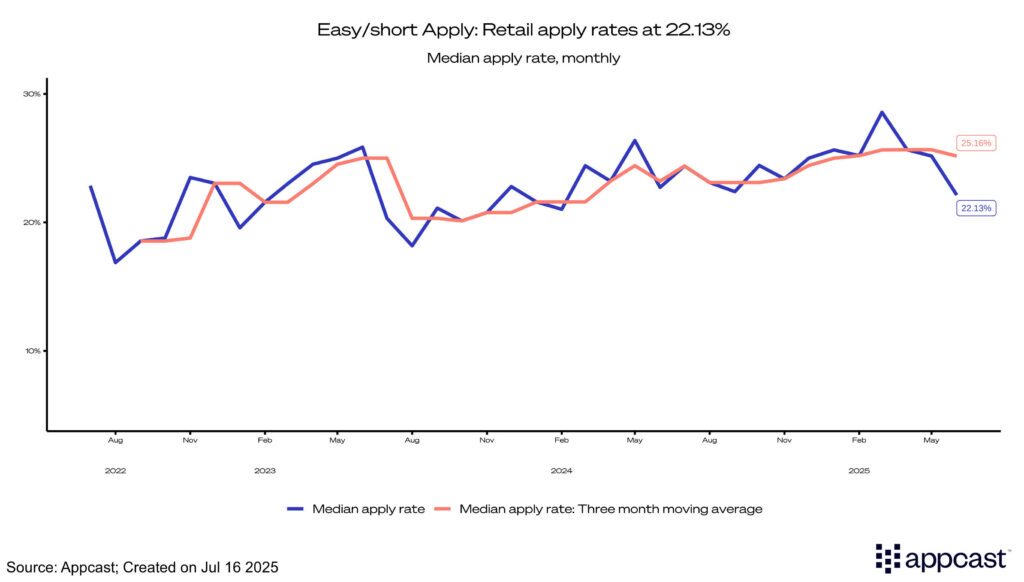
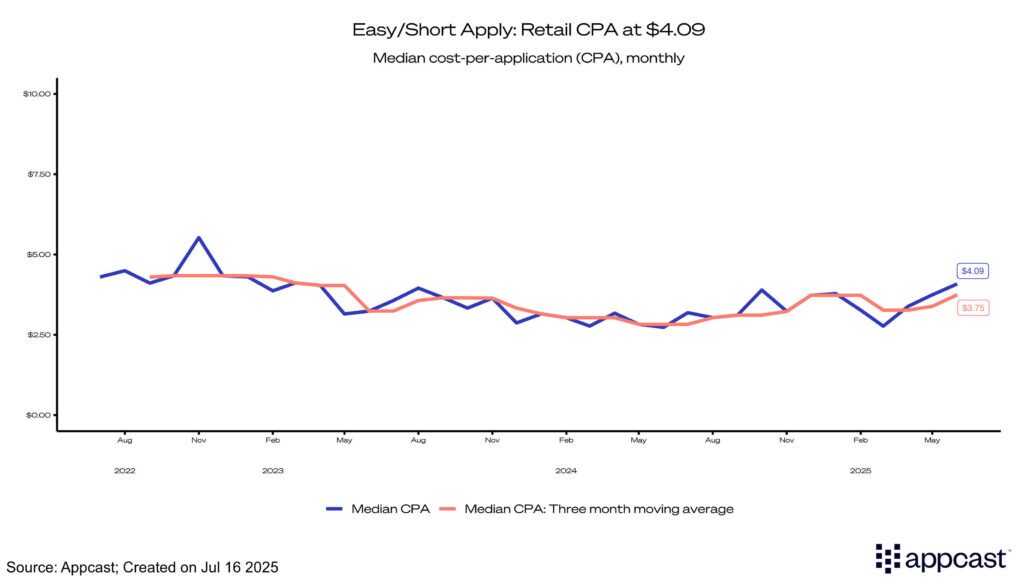
Recruiting costs for easy-apply methods portray upward trends but still remain low. CPCs rose to $1.24 while CPAs rose to just over $4, and the easy apply rate dropped significantly to just over 22% in June.
Recruitment Marketing Forecast
Our CPA forecast, based on the last two years of data, indicates that recruiting costs will remain stable, predicting that CPAs will stay in the $11 to 12$ range for the remainder of the year. However, with policy on tariffs shifts nearly daily, prices may change—in the greater economy and in the recruiting market—in response over the next six months.
What does this mean for recruiting in retail?
Retail recruiting still shows a mixed outlook for 2025. Since consumer demand remains relatively stable, there is potential for stability and growth, but due to the uncertain economic climate, the impacts of policy changes may negatively impact the sector. High long-apply rates suggest that recruitment costs will remain low. However, the decline in easy-apply rates could increase recruitment costs for easy-apply methods.
Hiring demand in retail decreased slightly after the first tariffs were introduced; however, it was able to hold strong. With tariff revisions promised for August 1st, hiring demand may decline over the course of 2025 depending on the outcome of these policies. Recruiters will likely see recruiting costs remain stable, as job growth slows in the sector over the course of the year.
Forecasting Methodology
Cost-per-application (CPA) is forecasted two quarters ahead using the previous two years’ worth of one-month moving average data. A combination of ARIMA, exponential smoothing, and seasonal naïve models are used to create an ensemble forecast. The forecast provides both the 95th percentile confidence intervals, indicating the likelihood that each value will be within the CPA range provided.